HETEGAN: Heterogeneous Parallel Inference for Large Language Models on Resource-Constrained Devices
arXiv
Xuanlei Zhao, Yang You
National University of Singapore
Background
When serving LLMs with limited GPU memory, Existing systems often offload some model parameters in CPU memory and transfer them to the GPU during inference, causing high latency due to the slow PCIe transfer.
Solution
HeteGen introduces a novel approach by utilizing the CPU not only for storage but also to offload part of the computation. Specifically, it employs heterogeneous tensor parallelism, splitting model computations between the CPU and GPU based on a pre-determined ratio. This ratio is designed to ensure that T(CPU) = T(GPU) + T(COM).
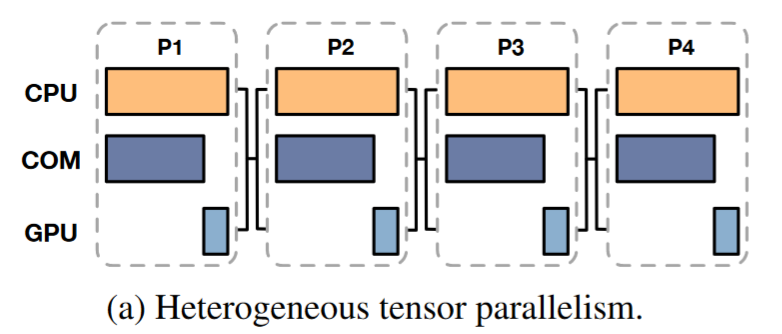
PS: While CPU computation is underway, model parameters are conveyed to the GPU. The GPU, in turn, generates results once the communication process is completed.
Some details
(1) The ratio is determined through profiling each module before inference and is applied at the granularity of individual linear layers, such as the Q, K, and V layers in Transformers, with each layer having its own optimized ratio.
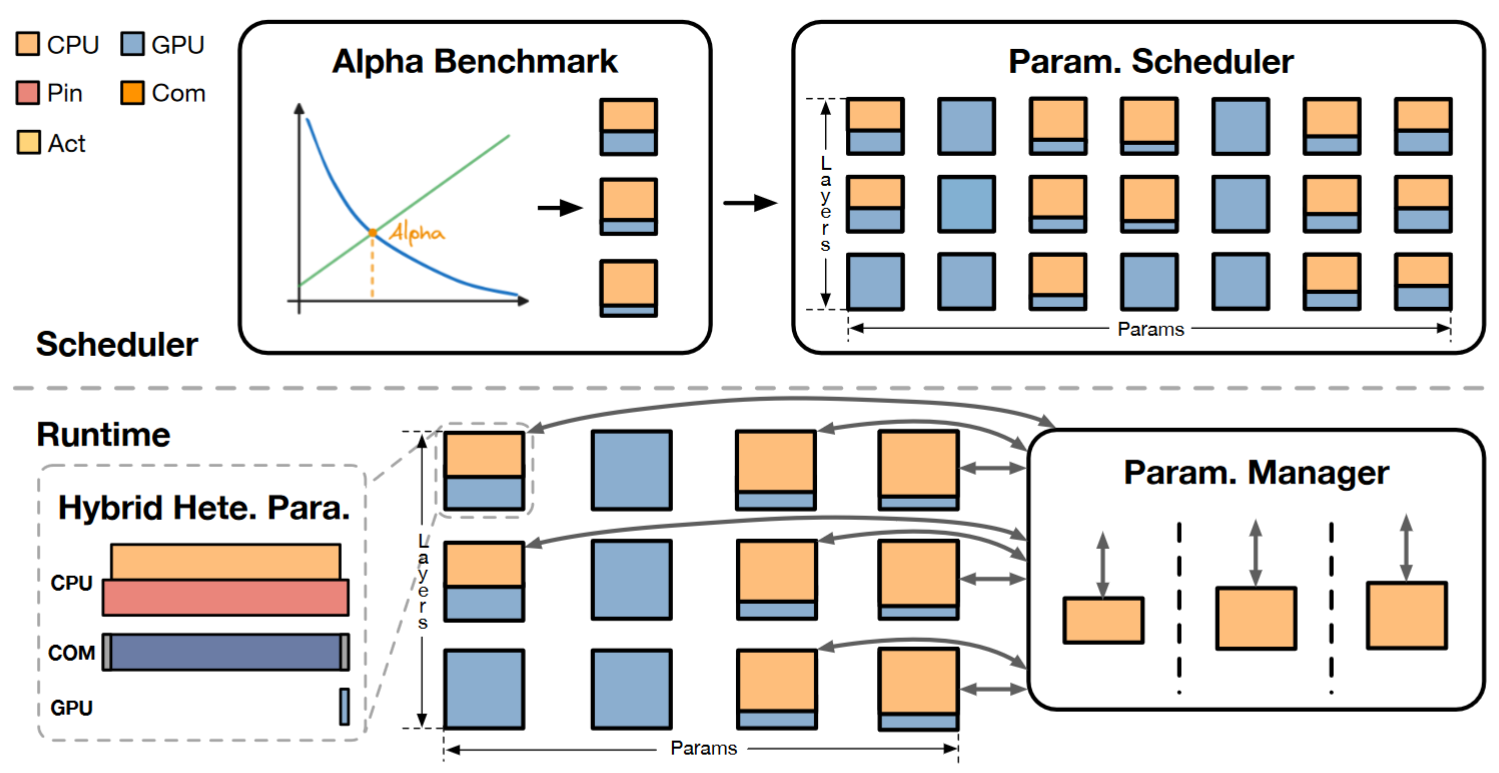
Optimization: (1) HeteGen also leverages pinned memory to improve concurrency (2) HeteGen dynamically transfers parameters from the CPU back to the GPU when additional GPU memory becomes available. The transfer priority is determined by the g=T(CPU)/M(GPU), where higher values indicate greater performance gains per unit of GPU memory used.
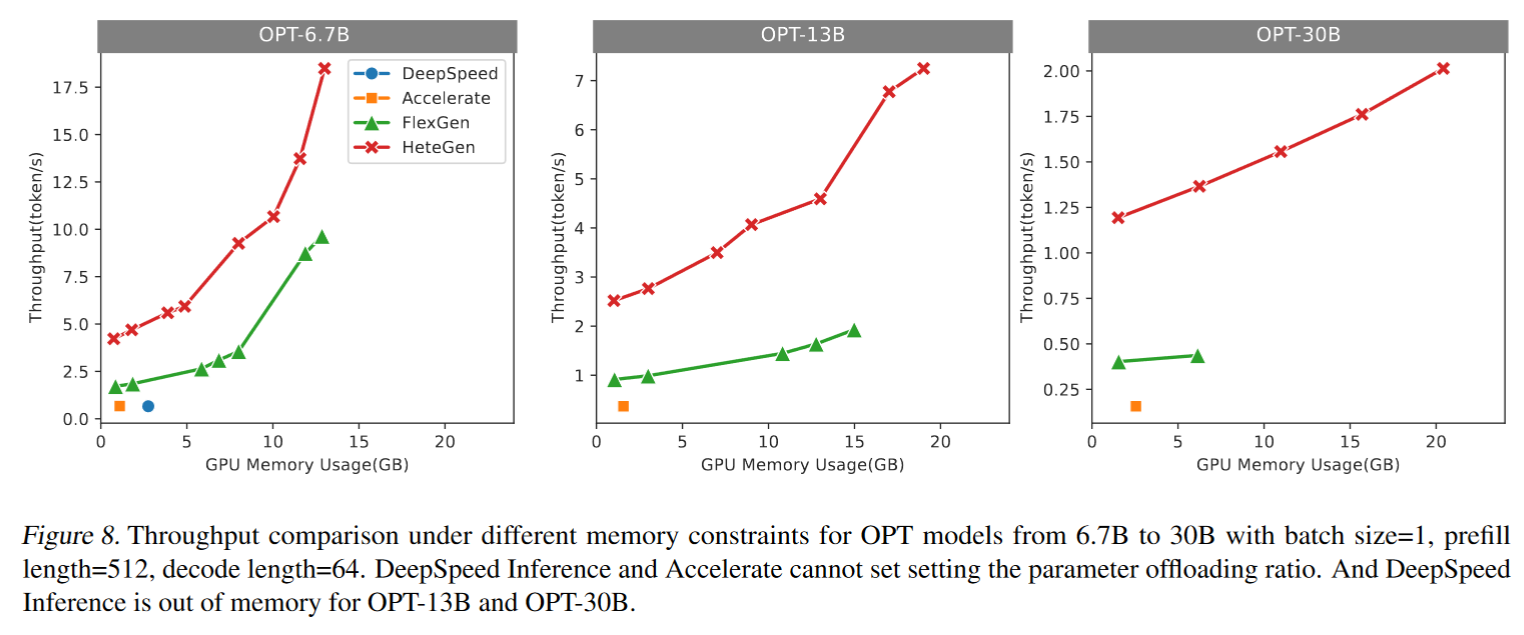
Evaluation
- NVIDIA A10(24GB) GPU.
- CPU cores at most 16.
- GPU and CPU communicate via PCIE.
Workload:
- prefill lengths 512, generated length 64, batch size 1
Metric: throughput of generating tokens under different scenarios