TwinPilots: A New Computing Paradigm for GPU-CPU Parallel LLM Inference
Systor 2024
Chengye Yu, Song Jiang
Chinese University of Hong Kong, University of Texas at Arlington
Background
When serving LLMs, GPU has insufficient memory and runs at a much slower speed due to constantly waiting for data to be loaded from the CPU memory via a slow PCIe bus.
Solution
Key Idea
Break down each transformer layer into a set of constituent operations and estimate the operations’ CPU execution time and GPU execution time (including the data’s loading time into GPU) BASED on the history time. Then determine operations should be executed on the CPU or GPU.
Profiling
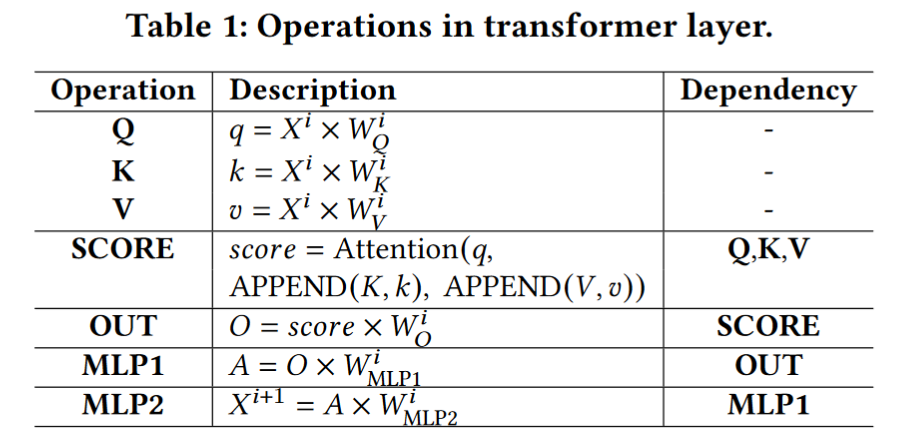
The data loading time does significantly surpass the GPU computing time!
Modeling
Model the operations placement problem as a load balancing problem:
- given a set ops containing 𝑁 operations and 2 devices: GPU and CPU
- the processing time of operation 𝑖 is 𝑔𝑝𝑢_𝑖 on GPU and 𝑐𝑝𝑢_𝑖 on CPU.
- 𝑑𝑒𝑣𝑖𝑐𝑒_𝑖 denote the computation device of operation 𝑖 (1 for CPU and 0 for GPU)
- total CPU processing time and GPU processing time of a certain plan 𝐷 = {𝑑𝑒𝑣𝑖𝑐𝑒_𝑖 ; 𝑖=1, . . .,𝑁 }
𝑆_𝑐𝑝𝑢 = SUM(𝑐𝑝𝑢_𝑖 × 𝑑𝑒𝑣𝑖𝑐𝑒_𝑖) and 𝑆_𝑔𝑝𝑢 = SUM(𝑔𝑝𝑢_𝑖 × (1−𝑑𝑒𝑣𝑖𝑐𝑒_𝑖)
The makespan 𝜆 of the plan is max(𝑆𝑐𝑝𝑢, 𝑆𝑔𝑝𝑢). The objective is to find a plan 𝐷 that minimizes the 𝜆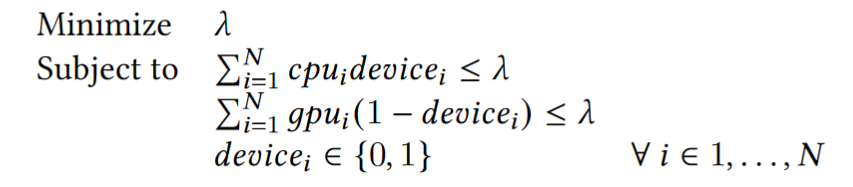
Note:the load balancing problem is NP-complete, but the small solution space is tolerable.
System Design
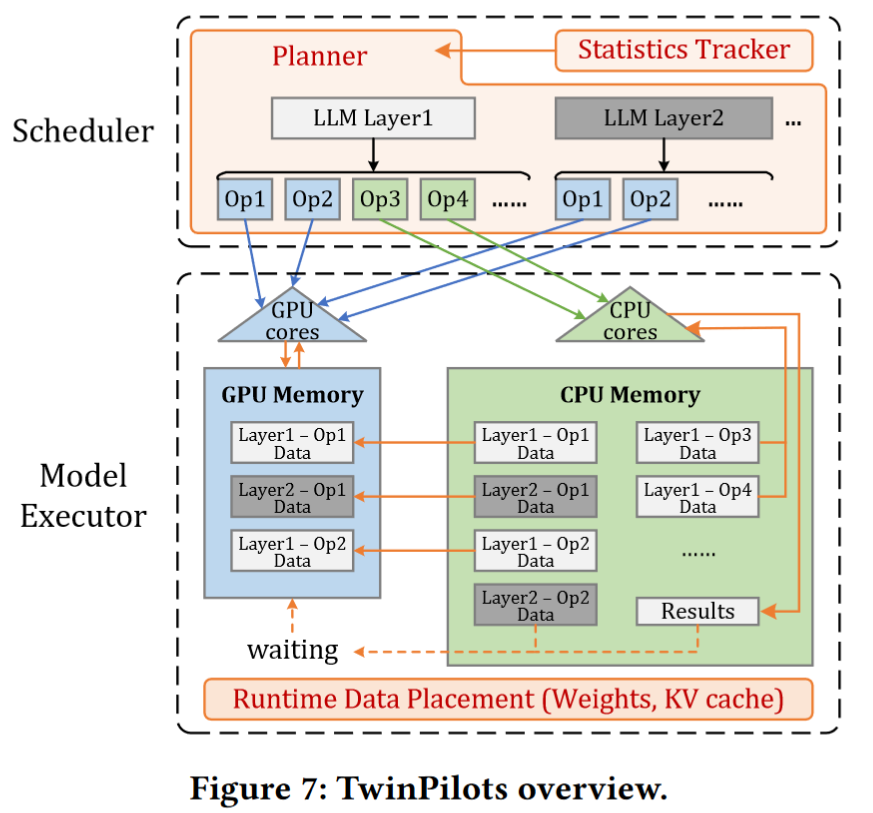
TwinPilots comprises an online scheduler and a model executor.
- online scheduler: collects historical execution info from statistics tracker and generates execution plans for each operation. (Statistics records are initiated by running several predefined batch sizes and sequence lengths offline)
- model executor: performs data prefetching and operation computation based on the plan, utilizing both CPU and GPU resources in a pipelined manner.
Further optimization
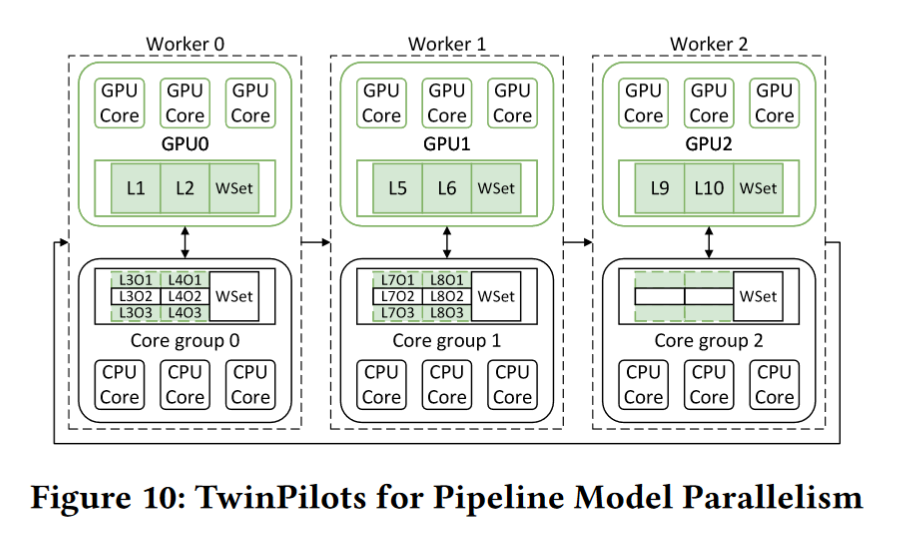
TwinPilots also support future pipeline parallelism on multiple GPUs by partitions CPU cores into distinct core groups. Each GPU collaborates with one CPU core group to form a worker, which handles a portion of consecutive layers. LLM layers are evenly distributed across workers.
Details
NOTE: 计算每个操作平均时间时要考虑batch_size和length(score操作)