Accelerating Distributed MoE Training and Inference with Lina
ATC ‘23
Jiamin Li, City University of Hong Kong; Yimin Jiang, ByteDance Inc.; Yibo Zhu, unaffiliated; Cong Wang, City University of Hong Kong; Hong Xu, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
Background
Existing MoE systems [DeepSpeed, Tutel, Gshard, …] allocate one unique compute device (e.g., GPU) for each expert in expert parallelism. An all-to-all communication is then needed to send tokens to their experts selected by the gating network, and another all-to-all is needed to send tokens back to the device they belong to in data parallelism to finish the rest of the forward pass.
Sites\zzxBlog\static\images\MOE\Lina_2.png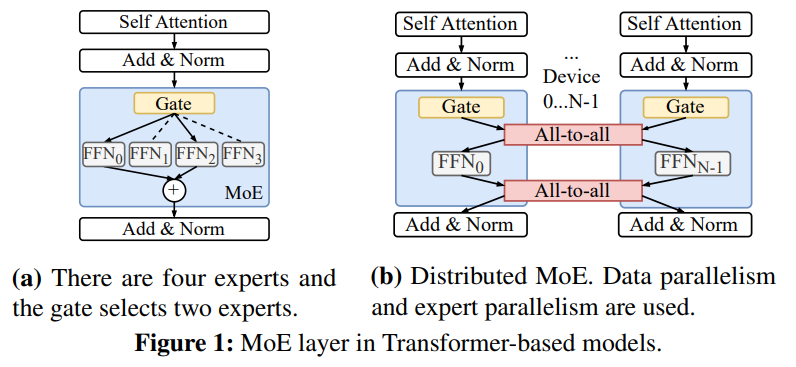

Problem
Distributed MoE training and inference is inefficient, mainly due to the interleaved all-to-all communication during model computation.
Problem in Training : Prolonged all-to-all with allreduce.
Problem in Inference: Skewed expert popularity. Within one batch, tokens to the less occupied experts have to wait for others to complete on the more popular experts, degrading the all-to-all performance significantly. Further, under uniform expert-device allocation, devices hosting popular experts have more tokens using their links for all-to-all, while the links of other devices are underutilized.
Solution
Exploit the expert selection pattern across adjacent layers to estimate the expert popularity.
They find that a token’s expert selection demonstrates a pattern across the MoE layers. Tokens that have selected the same expert in layer i tend to select the same expert again in layer i+1.
Dynamically schedule based on the estimation.
Based upon the estimation, Lina performs two-phase dynamically scheduling at each layer to allocate proportionally more devices for popular experts and pack unpopular ones to fewer devices, and coordinate all-to-all correspondingly.
Implementation
Lina is based on DeepSpeed MoE and PyTorch.
Evaluation
- Baseline: DeepSpeed
- Performance: Compared to the state-of-the-art system DeepSpeed, the median and 95%ile inference time is reduced by 1.45x and 1.63x.
Discussion
- Lina focuses on sparsely-activated MoE with data and expert parallelism, without considering pipeline and tensor parallelisms.
- Estimation of expert popularity: The current estimation approach used by Lina relies on data collection during the training stage. Accuracy and confidence also need further improvement.